Bài 3: Giới thiệu Patroni và etcd
Hiểu rõ Patroni hoạt động thế nào, vai trò của DCS (etcd/Consul/ZooKeeper), thuật toán Raft consensus và cơ chế tự động leader election.
Mục tiêu
Sau bài học này, bạn sẽ hiểu:
- Patroni là gì và cách hoạt động
- DCS (Distributed Configuration Store) - etcd/Consul/ZooKeeper
- Consensus algorithm (Raft)
- Leader election & Failover mechanism
- Split-brain problem và cách giải quyết
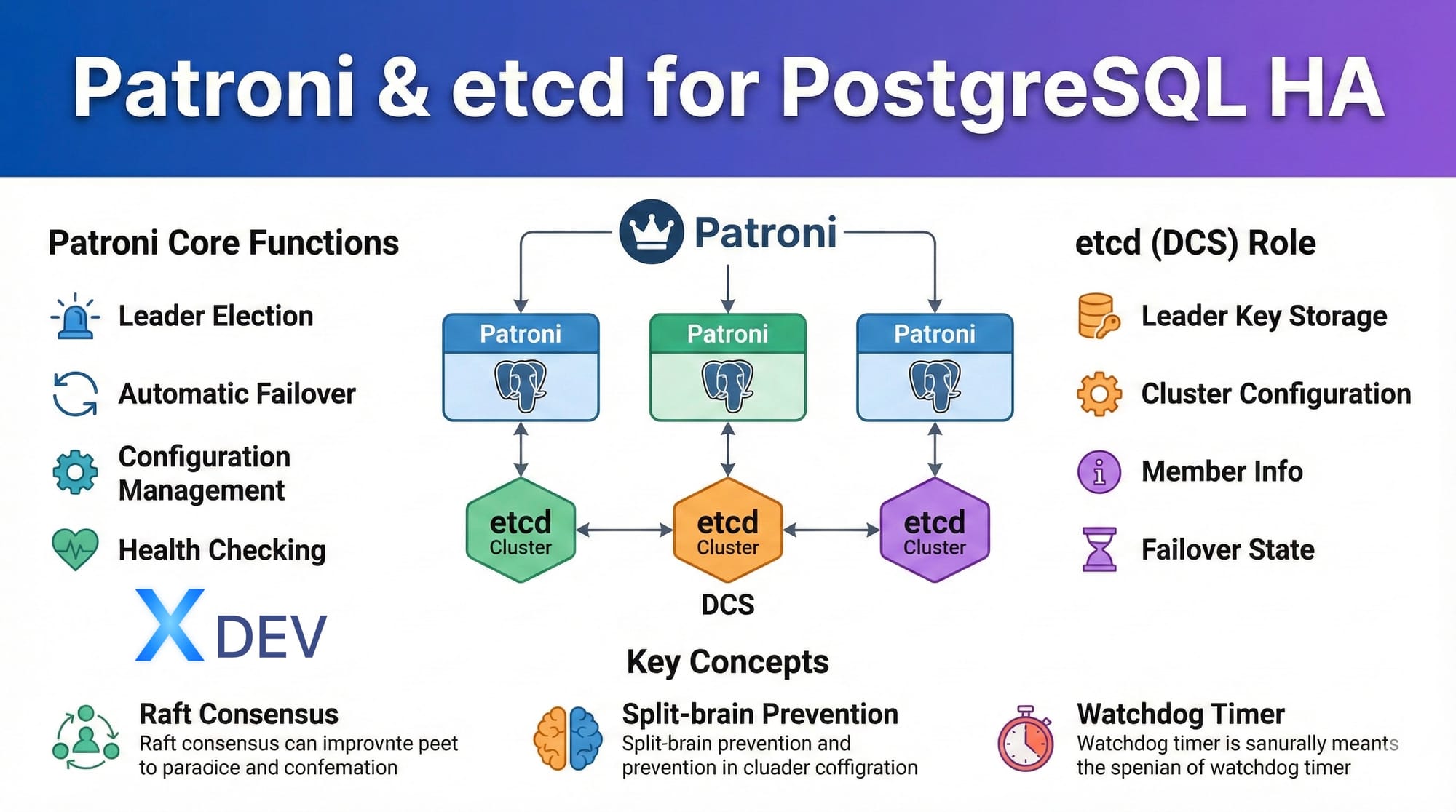
1. Patroni là gì?
Giới thiệu
Patroni là một template HA (High Availability) mã nguồn mở cho PostgreSQL, được phát triển bởi Zalando. Nó tự động hóa việc quản lý PostgreSQL cluster, bao gồm:
- Leader election: Tự động chọn primary node
- Automatic failover: Chuyển đổi dự phòng tự động khi primary bị lỗi
- Configuration management: Quản lý cấu hình tập trung
- Health checking: Giám sát sức khỏe của các nodes liên tục
Kiến trúc Patroni
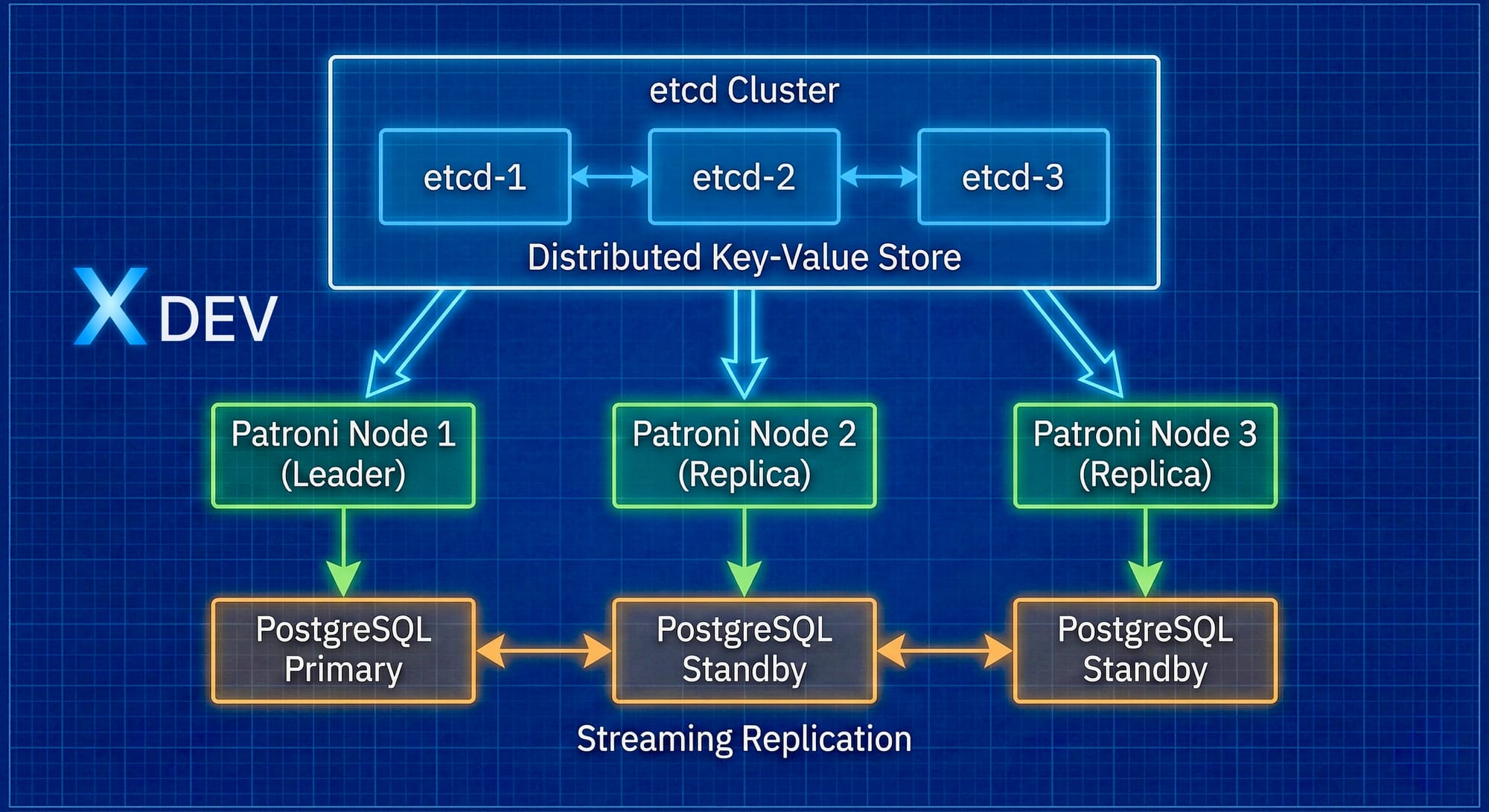
Cách hoạt động của Patroni
- Khởi động: Mỗi Patroni instance kết nối đến DCS (etcd)
- Leader election: Các node cạnh tranh để trở thành leader trong DCS
- Role assignment: Node giành được leader lock sẽ promote PostgreSQL thành primary
- Health monitoring: Patroni liên tục kiểm tra:
- PostgreSQL process health
- Replication status
- DCS connectivity
- Auto failover: Nếu leader bị lỗi, Patroni tự động:
- Phát hiện sự cố
- Chọn replica phù hợp nhất
- Promote replica mới thành primary
- Cập nhật các replica còn lại
Các thành phần chính
Patroni daemon
- Chạy trên mỗi PostgreSQL node
- Quản lý lifecycle của PostgreSQL
- Thực hiện health checks
- Tương tác với DCS
REST API
- Endpoint cho health checks:
http://node:8008/health - Endpoint cho read-only:
http://node:8008/read-only - Endpoint cho primary:
http://node:8008/master(deprecated) hoặc/primary
patronictl
- CLI tool để quản lý cluster
- Commands: list, switchover, failover, reinit, restart, reload
2. DCS - Distributed Configuration Store
Vai trò của DCS
DCS là trung tâm điều phối cho Patroni cluster, lưu trữ:
- Leader key: Thông tin node nào đang là leader (TTL-based)
- Configuration: Cấu hình PostgreSQL và Patroni
- Member information: Danh sách các nodes trong cluster
- Failover/Switchover state: Trạng thái chuyển đổi
So sánh các DCS phổ biến
| Tính năng | etcd | Consul | ZooKeeper |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ngôn ngữ | Go | Go | Java |
| Consensus | Raft | Raft | ZAB (Paxos-like) |
| API | gRPC, HTTP | HTTP, DNS | Custom protocol |
| Setup | Đơn giản | Trung bình | Phức tạp |
| Performance | Cao | Cao | Trung bình |
| Tài liệu | Tốt | Rất tốt | Trung bình |
| Sử dụng | Kubernetes, Patroni | Service mesh, HA | Hadoop, Kafka |
Khuyến nghị: etcd cho hầu hết các trường hợp vì đơn giản và hiệu năng cao.
etcd - Distributed Key-Value Store
Đặc điểm chính:
- Strongly consistent (CAP theorem: CP)
- Distributed và highly available
- Fast (sub-millisecond latency)
- Simple API
- Watch mechanism cho real-time updates
Cấu trúc dữ liệu trong etcd cho Patroni:
/service/postgres/
├── config # Cấu hình cluster
├── initialize # Bootstrap token
├── leader # Leader lock (TTL: 30s)
├── members/
│ ├── node1 # Thông tin node1
│ ├── node2 # Thông tin node2
│ └── node3 # Thông tin node3
├── optime/
│ └── leader # LSN của leader
└── failover # Failover/switchover instructions
3. Consensus Algorithm - Raft
Raft là gì?
Raft là thuật toán consensus được thiết kế để dễ hiểu hơn Paxos, đảm bảo:
- Safety: Không bao giờ trả về kết quả sai
- Liveness: Luôn có tiến triển (khi majority nodes hoạt động)
- Consistency: Tất cả nodes nhìn thấy cùng một trạng thái
Các vai trò trong Raft
- Leader:
- Xử lý tất cả client requests
- Replicate log entries đến followers
- Duy nhất trong một term
- Follower:
- Passive, chỉ nhận requests từ leader
- Nếu không nhận heartbeat, trở thành candidate
- Candidate:
- Follower timeout thành candidate
- Request votes từ các nodes khác
- Nếu thắng bầu cử → Leader
Quy trình Leader Election
Chi tiết bầu cử:
- Follower không nhận heartbeat trong election timeout (150-300ms ngẫu nhiên)
- Chuyển thành Candidate, tăng term number
- Vote cho chính mình
- Gửi RequestVote RPC đến tất cả nodes
- Nếu nhận được majority votes (n/2 + 1):
- Trở thành Leader
- Gửi heartbeat ngay lập tức
- Nếu timeout hoặc thua cuộc:
- Quay lại Follower hoặc bắt đầu election mới
Quorum và Majority
Quorum: Số lượng nodes tối thiểu cần để hệ thống hoạt động
Cluster size | Quorum | Tolerated failures
-------------|--------|-------------------
1 | 1 | 0
3 | 2 | 1
5 | 3 | 2
7 | 4 | 3
Công thức: Quorum = floor(n/2) + 1
Ví dụ với 3 nodes:
- ✅ 3 nodes active: Cluster healthy
- ✅ 2 nodes active: Cluster works (quorum met)
- ❌ 1 node active: Cluster stops (no quorum)
Khuyến nghị: Luôn dùng số lẻ nodes (3, 5, 7) để tối ưu fault tolerance.
4. Leader Election trong Patroni
Cơ chế Leader Lock
Patroni sử dụng DCS để implement distributed lock:
Leader Lock Properties:
Key: /service/postgres/leader
Value:
{
"version": "3.0.2",
"conn_url": "postgres://node1:5432/postgres",
"api_url": "http://node1:8008/patroni",
"xlog_location": 123456789,
"timeline": 2
}
TTL: 30 seconds
Quy trình Leader Election
Bước 1: Race Condition
Time: T0 - Leader crashes
Node1: Check DCS → No leader key exists
Node2: Check DCS → No leader key exists
Node3: Check DCS → No leader key exists
Bước 2: Acquire Lock Attempt
Time: T0 + 100ms
Node1: Try acquire lock → SUCCESS (first to write)
Node2: Try acquire lock → FAILED (key exists)
Node3: Try acquire lock → FAILED (key exists)
Bước 3: Role Assignment
Node1: Promote PostgreSQL to Primary
Node2: Configure as Replica, point to Node1
Node3: Configure as Replica, point to Node1
Bước 4: Maintenance
Every 10 seconds:
Node1 (Leader):
- Renew lock (TTL extension)
- Update xlog_location
- Send heartbeat
Node2/3 (Followers):
- Monitor leader key
- Check replication lag
- Ready to take over
Tiêu chí chọn Best Replica
Khi failover, Patroni chọn replica dựa trên:
- Replication state:
streaming>in archive recovery
- Timeline: Timeline cao hơn được ưu tiên
- XLog position:
- Replica có LSN gần primary nhất
- Ít data loss nhất
- No replication lag:
pg_stat_replication.replay_lag = 0
- Explicit candidate: Set trong configuration
Priority tag:
tags:
nofailover: false
noloadbalance: false
clonefrom: false
nosync: false
Ví dụ:
Primary fails at LSN: 0/3000000
Replica1: LSN=0/3000000, lag=0s ← BEST CHOICE
Replica2: LSN=0/2FFFFFF, lag=1s
Replica3: LSN=0/2FFFFFE, lag=2s
→ Patroni promotes Replica1
5. Failover Mechanism
Automatic Failover Process
Timeline chi tiết:
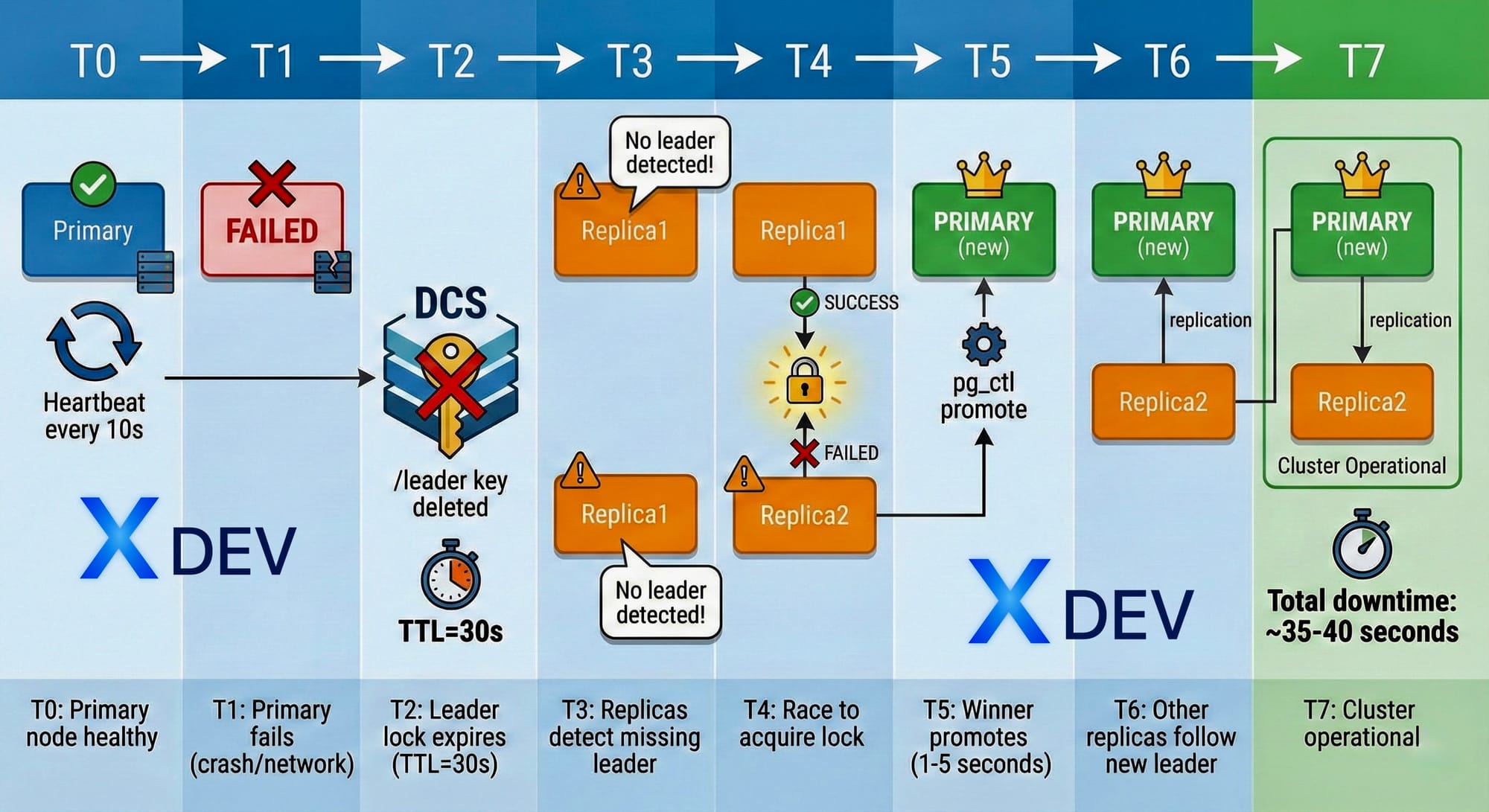
Các bước failover chi tiết
Step 1: Detect failure
# Patroni health check loop
while True:
if not check_postgresql_health():
log.error("PostgreSQL unhealthy")
stop_renewing_leader_lock()
if not check_dcs_connectivity():
log.error("Lost connection to DCS")
demote_if_leader()
sleep(10)
Step 2: Leader lock expires
# In etcd
$ etcdctl get /service/postgres/leader
# After TTL: Key not found
# Patroni logs on former leader
WARN: Could not renew leader lock
INFO: Demoting PostgreSQL to standby
Step 3: Replica promotion
# Patroni on promoted replica
INFO: No leader found
INFO: Attempting to acquire leader lock
INFO: Lock acquired successfully
INFO: Promoting PostgreSQL instance
INFO: Updating configuration
INFO: Notifying other members
Step 4: Reconfiguration
-- On promoted replica
SELECT pg_promote();
-- Changes primary_conninfo to null
-- Restarts as read-write
Step 5: Followers repoint
# Other replicas
INFO: New leader detected: node2
INFO: Updating primary_conninfo
INFO: Restarting replication
Monitoring Failover
Các metrics quan trọng:
patroni_primary_timeline: Phát hiện timeline changespatroni_xlog_location: Theo dõi WAL positionpatroni_replication_lag: Lag trước failoverpatroni_failover_count: Đếm số lần failover
6. Split-Brain Problem
Split-Brain là gì?
Định nghĩa: Tình huống có ≥2 nodes nghĩ mình là Primary, ghi dữ liệu khác nhau → Data divergence.
Nguyên nhân
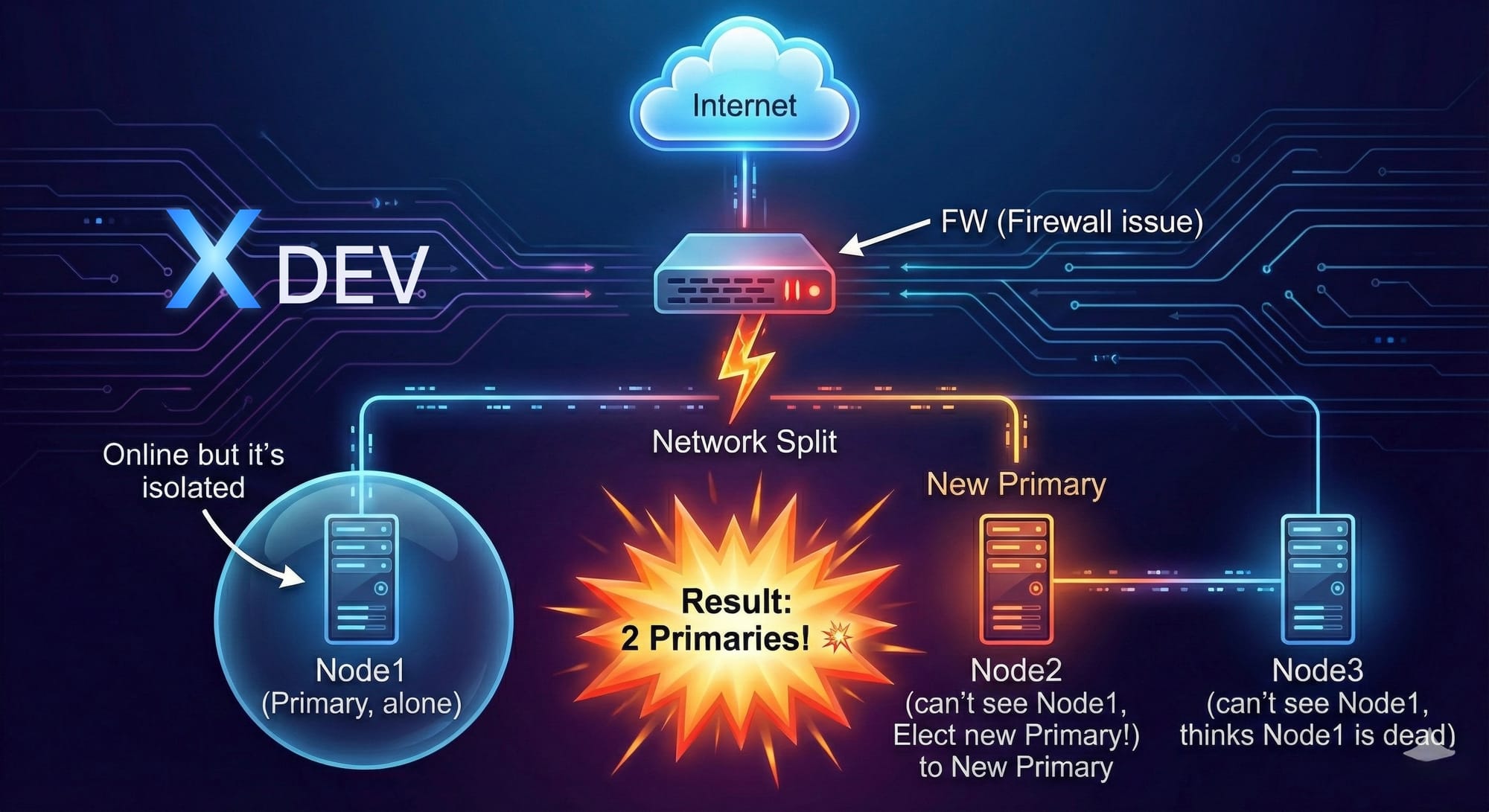
- Network Partition
- DCS partition: etcd cluster split
- Slow network: Heartbeat timeout nhưng node vẫn sống
Hậu quả của Split-Brain
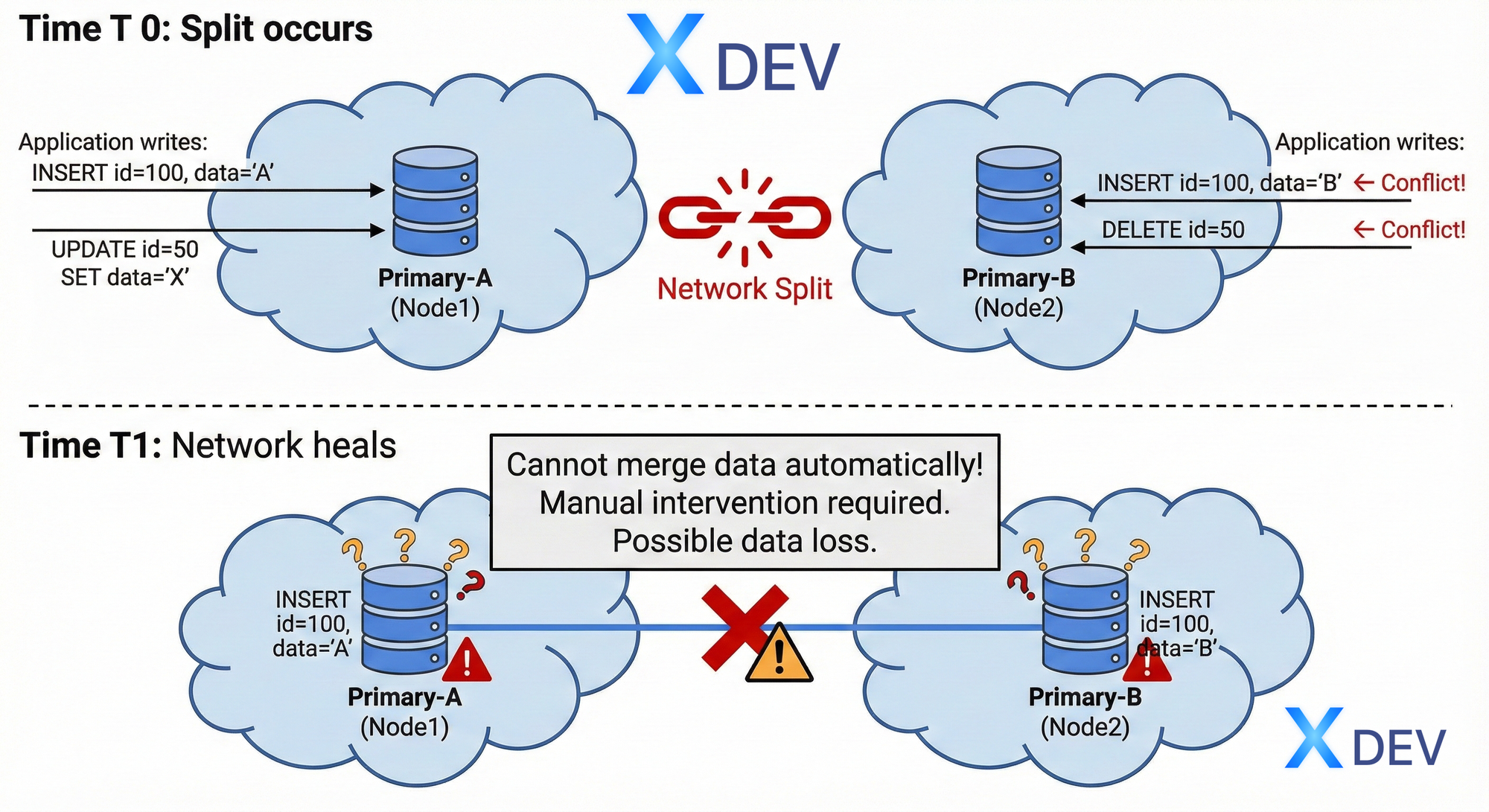
Patroni's Split-Brain Prevention
Cơ chế 1: DCS-based Lock (Primary)
def maintain_leader_lock():
while is_leader:
# Must renew within TTL
success = dcs.renew_lock(ttl=30)
if not success:
log.critical("Lost leader lock!")
# Immediate demotion
demote_to_standby()
stop_accepting_writes()
break
sleep(10)
Cơ chế 2: Leader Key Verification
def before_handle_write():
leader_key = dcs.get("/service/postgres/leader")
if leader_key.owner != my_node_name:
# I'm not the real leader!
raise Exception("Not leader anymore")
demote_immediately()
Cơ chế 3: Timeline Divergence Detection
-- PostgreSQL timeline
SELECT timeline_id FROM pg_control_checkpoint();
-- If timelines diverge:
-- Node1: timeline=5
-- Node2: timeline=6
-- → Data inconsistency detected
-- → Requires pg_rewind or rebuild
Quorum requirement
etcd với 3 nodes:
Scenario 1: Network partition 1-2 split
Partition A: Node1 (1 node)
- Cannot get quorum (1 < 2)
- Cannot write to etcd
- Demotes to standby ✓
Partition B: Node2, Node3 (2 nodes)
- Has quorum (2 ≥ 2)
- Can elect leader
- Node2 becomes primary ✓
Result: Only 1 primary exists ✓
Scenario 2: Complete isolation
Node1: Isolated, loses DCS
- Tries to renew lock → FAIL
- Demotes PostgreSQL immediately
- Stops accepting connections
Node2/3: See Node1 gone
- Elect new leader
- Only 1 primary in cluster ✓
Watchdog Timer (Advanced Protection)
Hardware watchdog:
# patroni.yml
watchdog:
mode: required # or automatic, off
device: /dev/watchdog
safety_margin: 5
Hoạt động:
- Patroni kicks watchdog device every 10s
- If Patroni hangs or loses DCS → stops kicking
- After timeout → Watchdog reboots entire node
- Prevents "zombie primary" scenario
Best Practices để tránh Split-Brain
- Deploy DCS riêng biệt: etcd cluster ở các AZ khác nhau
- Monitor DCS health: Alert khi etcd không khỏe
- Network redundancy: Nhiều đường network giữa nodes
- Proper timeouts:
patroni:
ttl: 30 # Leader lock TTL
loop_wait: 10 # Check interval
retry_timeout: 10 # DCS operation timeout
- Enable watchdog: Hardware protection layer
- Monitoring:
# Check for timeline divergence
patronictl list
# Expected: All nodes same timeline
+ Cluster: postgres (7001234567890123456) ----+----+-----------+
| Member | Host | Role | State | TL | Lag in MB |
+--------+--------------+---------+---------+----+-----------+
| node1 | 10.0.1.1:5432| Leader | running | 5 | |
| node2 | 10.0.1.2:5432| Replica | running | 5 | 0 |
| node3 | 10.0.1.3:5432| Replica | running | 5 | 0 |
+--------+--------------+---------+---------+----+-----------+
Recovery từ Split-Brain
Nếu xảy ra split-brain:
Step 1: Identify
# Check timeline
patronictl list
# node1: timeline=5
# node2: timeline=6 ← DIVERGED!
Step 2: Choose primary
- Chọn node có data quan trọng hơn
- Hoặc node có timeline cao hơn
Step 3: Rebuild diverged replica
# Option 1: pg_rewind (if safe)
patronictl reinit postgres node2
# Option 2: Full rebuild
patronictl remove postgres node2
# Then: reinitialize from scratch
Step 4: Verify
patronictl list
# All nodes same timeline ✓
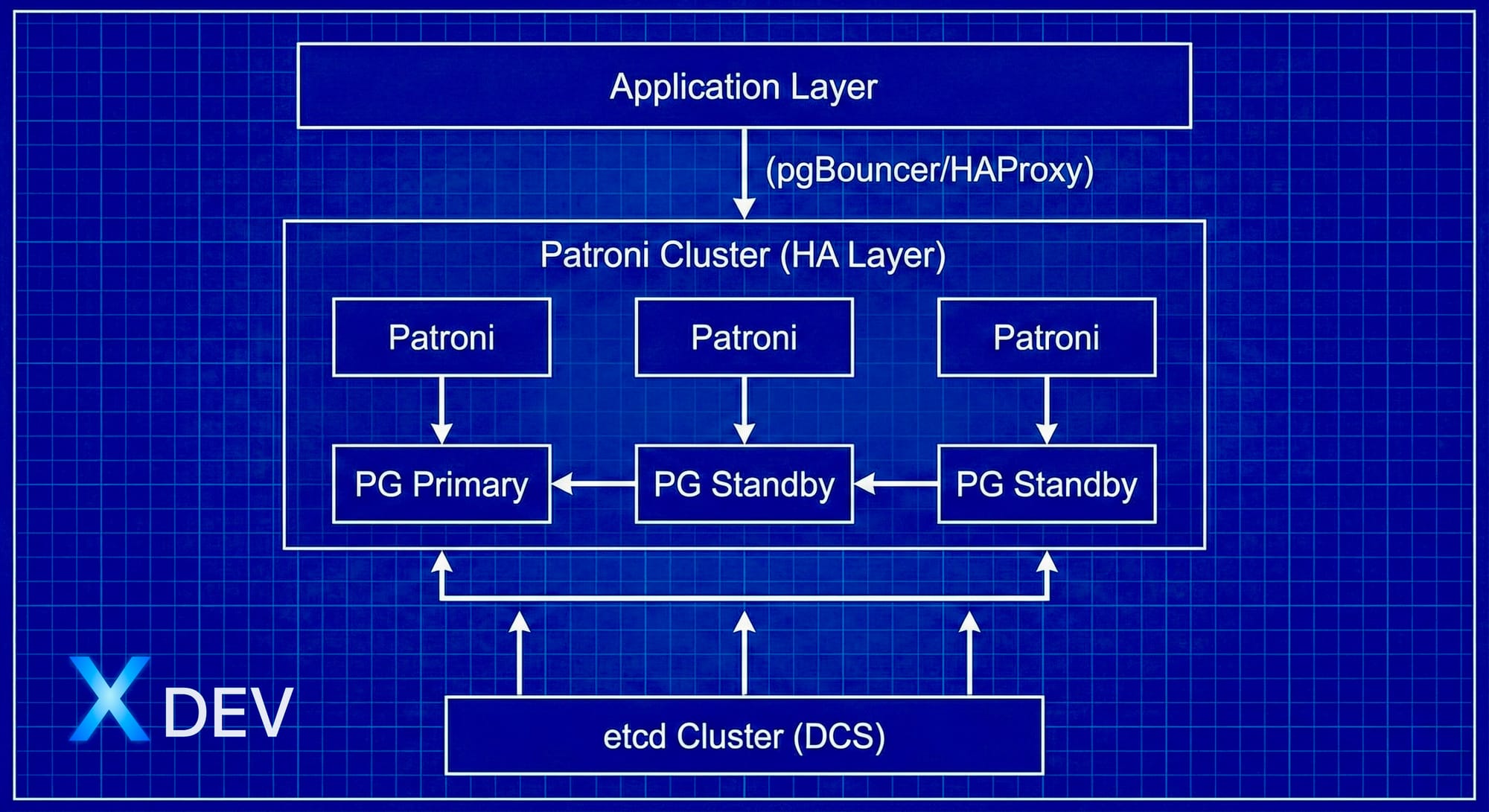
7. Tổng kết
Key Takeaways
✅ Patroni: Template HA tự động hóa quản lý PostgreSQL cluster
✅ DCS (etcd): Distributed coordination, store configuration và leader lock
✅ Raft consensus: Đảm bảo consistency và leader election trong etcd
✅ Leader election: Automatic, fast (~30-40s), based on TTL locks
✅ Failover: Tự động promote replica tốt nhất khi primary fails
✅ Split-brain prevention: DCS quorum + TTL locks + watchdog
Kiến trúc tổng hợp
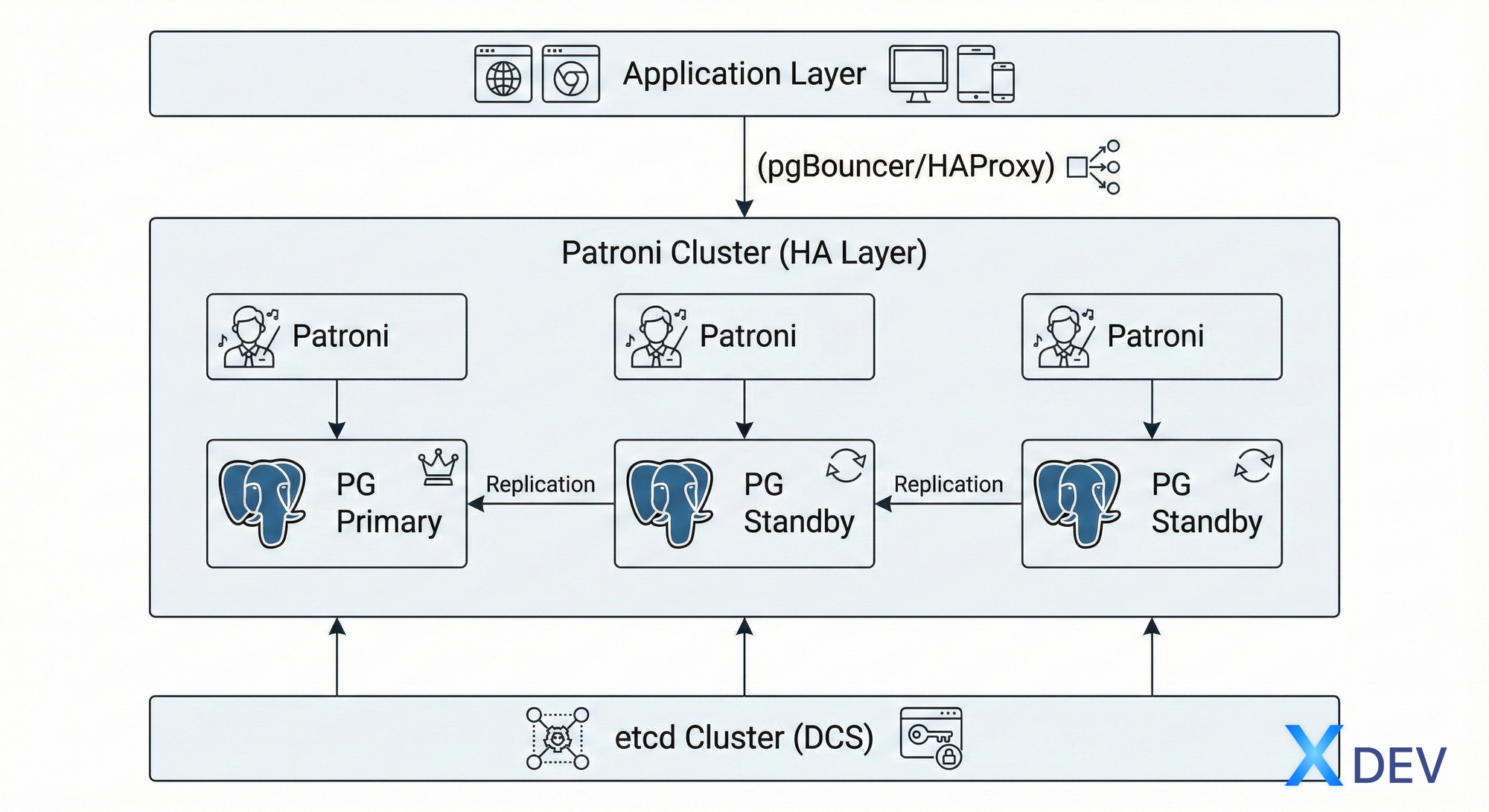
Câu hỏi ôn tập
- Patroni khác gì với Streaming Replication thuần?
- Tại sao cần DCS? Không thể dùng database để lưu state được không?
- Quorum trong cluster 5 nodes là bao nhiêu?
- Patroni chọn replica nào để promote khi failover?
- Split-brain xảy ra như thế nào và Patroni ngăn chặn ra sao?
- Timeline trong PostgreSQL có ý nghĩa gì?
- TTL 30 seconds nghĩa là gì? Tại sao không set TTL = 5 seconds?
Chuẩn bị cho bài tiếp theo
Bài 4 sẽ hướng dẫn chuẩn bị hạ tầng:
- Setup 3 VMs/Servers
- Cấu hình network, firewall
- SSH keys, time sync
- Dependencies cần thiết

