Bài 2: Streaming Replication trong PostgreSQL
Khám phá cơ chế Streaming Replication, WAL logging, sự khác biệt Synchronous/Asynchronous replication và thực hành setup Primary-Standby cơ bản.
Mục tiêu bài học
Sau bài học này, bạn sẽ:
- Hiểu sâu về cơ chế Streaming Replication trong PostgreSQL
- Nắm vững Write-Ahead Logging (WAL) và vai trò của nó
- Phân biệt Synchronous và Asynchronous Replication
- Hiểu và sử dụng Replication Slots
- Thực hành setup replication thủ công (Primary-Standby)
1. Cơ chế hoạt động của Streaming Replication
1.1. Tổng quan
Streaming Replication là phương pháp PostgreSQL replicate dữ liệu từ Primary server sang một hoặc nhiều Standby servers theo thời gian thực.
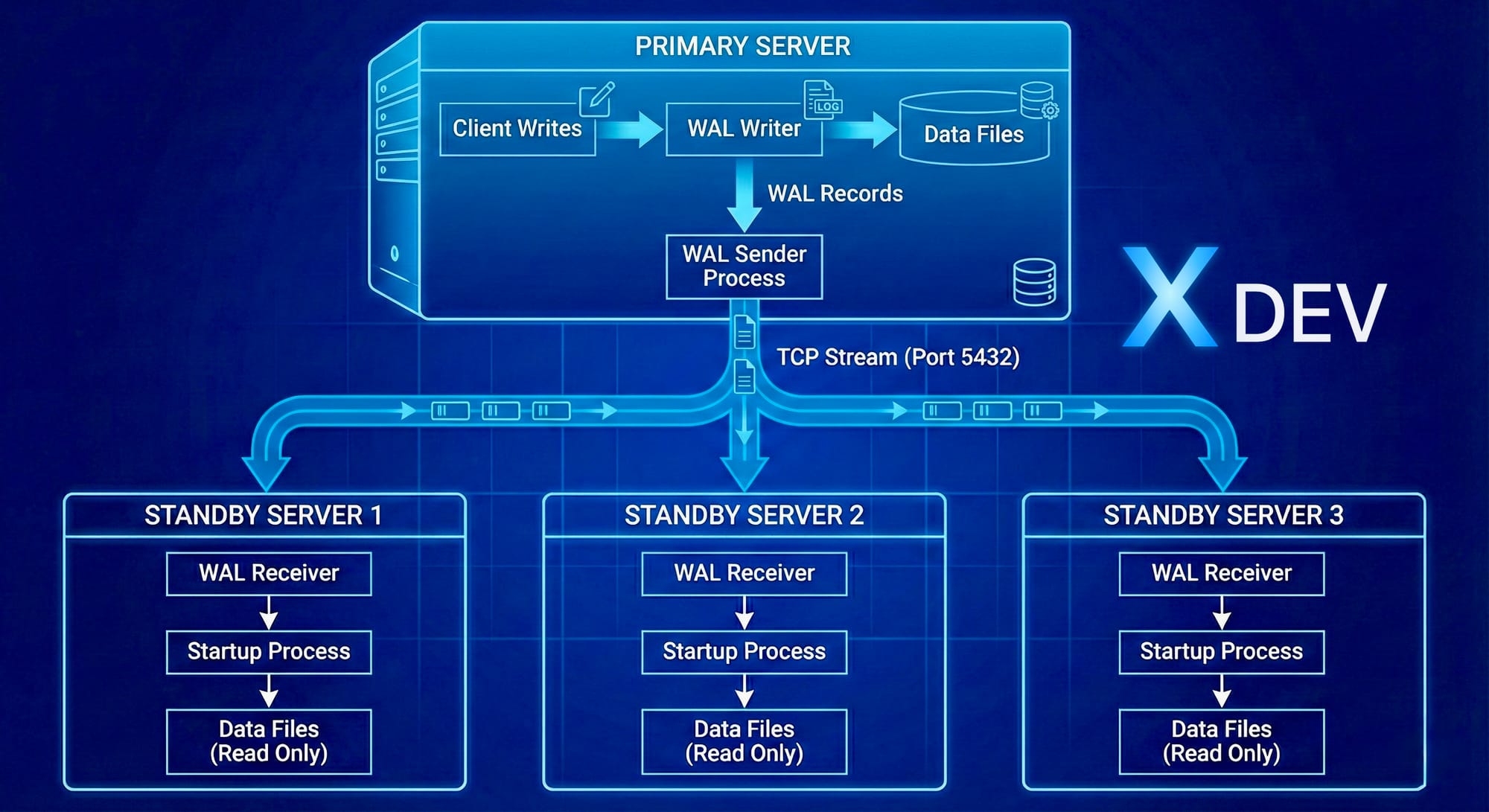
1.2. Các thành phần chính
WAL Sender (trên Primary)
- Process chuyên gửi WAL records đến Standby
- Một WAL sender cho mỗi Standby connection
- Monitoring:
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_replication;
WAL Receiver (trên Standby)
- Process nhận WAL records từ Primary
- Ghi WAL vào local WAL files
- Gửi feedback về Primary (LSN position, status)
Startup Process (trên Standby)
- Replay WAL records vào data files
- Giống như recovery process
- Có thể phục vụ read queries (Hot Standby)
1.3. Luồng dữ liệu chi tiết
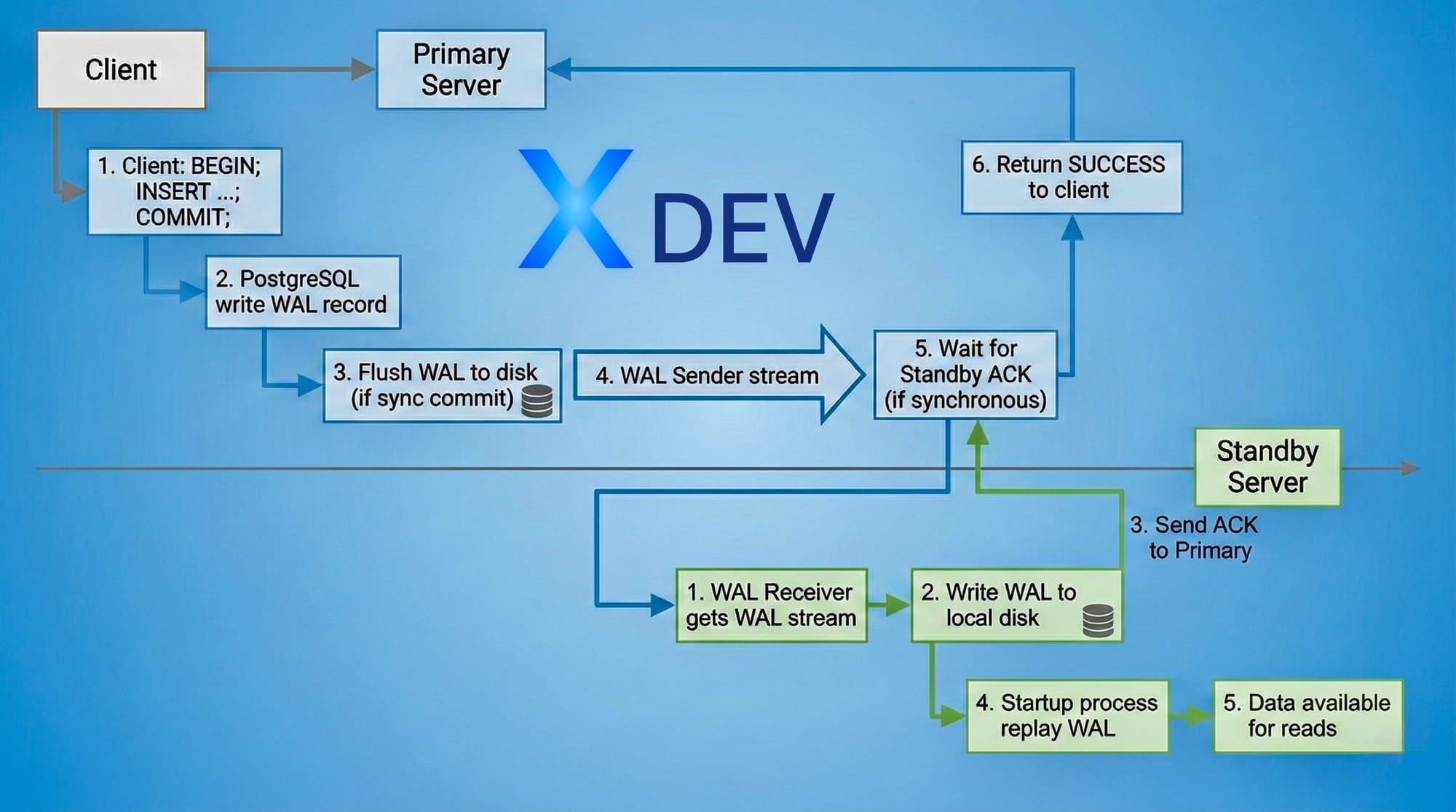
Thời gian thực tế:
- Asynchronous: ~0-100ms lag
- Synchronous: ~1-10ms lag (tùy network latency)
2. Write-Ahead Logging (WAL)
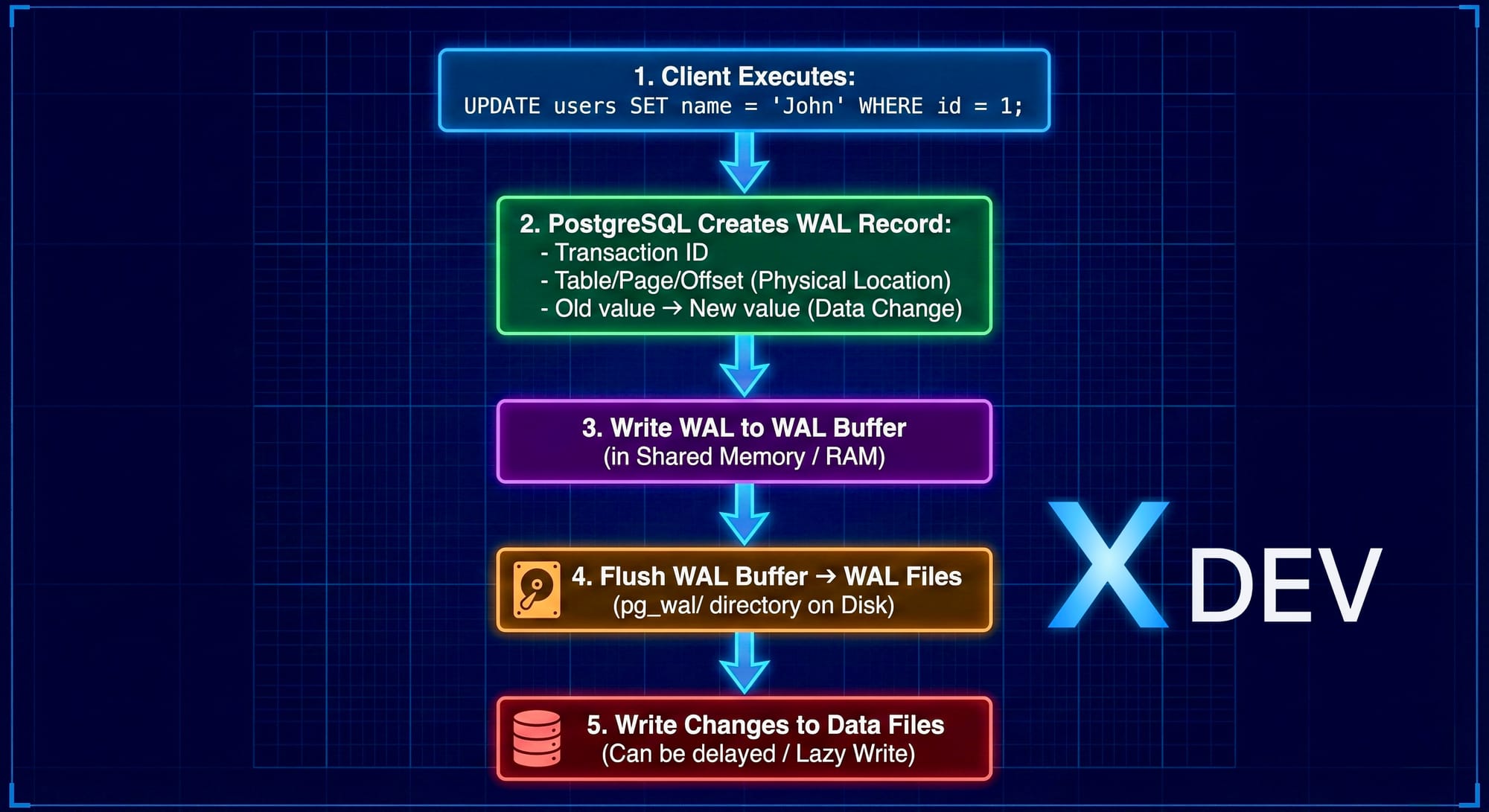
2.1. WAL là gì?
Write-Ahead Logging là kỹ thuật logging trong đó:
"Mọi thay đổi phải được ghi vào log TRƯỚC KHI ghi vào data files"
Nguyên tắc WAL:
2.2. WAL Files Structure
Vị trí: $PGDATA/pg_wal/
$ ls -lh $PGDATA/pg_wal/
-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M Nov 24 10:00 000000010000000000000001
-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M Nov 24 10:15 000000010000000000000002
-rw------- 1 postgres postgres 16M Nov 24 10:30 000000010000000000000003Đặc điểm:
- Mỗi file: 16MB (default)
- Tên file: Timeline ID + Segment Number
- Format:
TTTTTTTTXXXXXXXXYYYYYYYY- TTTTTTTT: Timeline (8 hex digits)
- XXXXXXXX: Log file number (8 hex)
- YYYYYYYY: Segment number (8 hex)
2.3. LSN (Log Sequence Number)
LSN là vị trí trong WAL stream, format: X/Y
- X: WAL file number
- Y: Offset trong file
-- Kiểm tra LSN hiện tại
SELECT pg_current_wal_lsn(); -- Primary
-- Output: 0/3000060
SELECT pg_last_wal_receive_lsn(); -- Standby (received)
SELECT pg_last_wal_replay_lsn(); -- Standby (applied)2.4. WAL Configuration Parameters
# postgresql.conf
# WAL Settings
wal_level = replica # minimal, replica, or logical
# replica: cho streaming replication
wal_log_hints = on # Cần thiết cho pg_rewind
# WAL Writing
wal_buffers = 16MB # WAL buffer size trong shared memory
wal_writer_delay = 200ms # WAL writer sleep time
# WAL Files Management
min_wal_size = 80MB # Tối thiểu WAL files giữ lại
max_wal_size = 1GB # Trigger checkpoint khi vượt
# Checkpoints
checkpoint_timeout = 5min # Tối đa giữa 2 checkpoints
checkpoint_completion_target = 0.9 # Spread checkpoint writes2.5. WAL và Crash Recovery
Khi PostgreSQL crash:
1. Server restart
2. PostgreSQL đọc last checkpoint location
3. Replay tất cả WAL records từ checkpoint → crash point
4. Khôi phục database về trạng thái consistent
5. Ready to accept connectionsVí dụ:
Timeline:
10:00 ─── Checkpoint ─── 10:05 ─── 10:08 (CRASH)
(LSN: 0/1000) (LSN: 0/3000)
Recovery:
- Bắt đầu từ LSN 0/1000
- Replay WAL → LSN 0/3000
- Database consistent tại 10:083. Synchronous vs Asynchronous Replication
3.1. Asynchronous Replication (Default)
Cách hoạt động:

Đặc điểm:
- ✅ Performance cao: Primary không đợi Standby
- ✅ Latency thấp: Commit time không phụ thuộc network
- ❌ Có thể mất data: Nếu Primary crash trước khi Standby nhận WAL
- ❌ RPO > 0: Recovery Point Objective không phải zero
Configuration:
# postgresql.conf (Primary)
synchronous_commit = off # hoặc localUse cases:
- Standby ở datacenter khác (high latency)
- Ưu tiên performance hơn data safety
- Acceptable data loss (vài giây)
3.2. Synchronous Replication
Cách hoạt động:
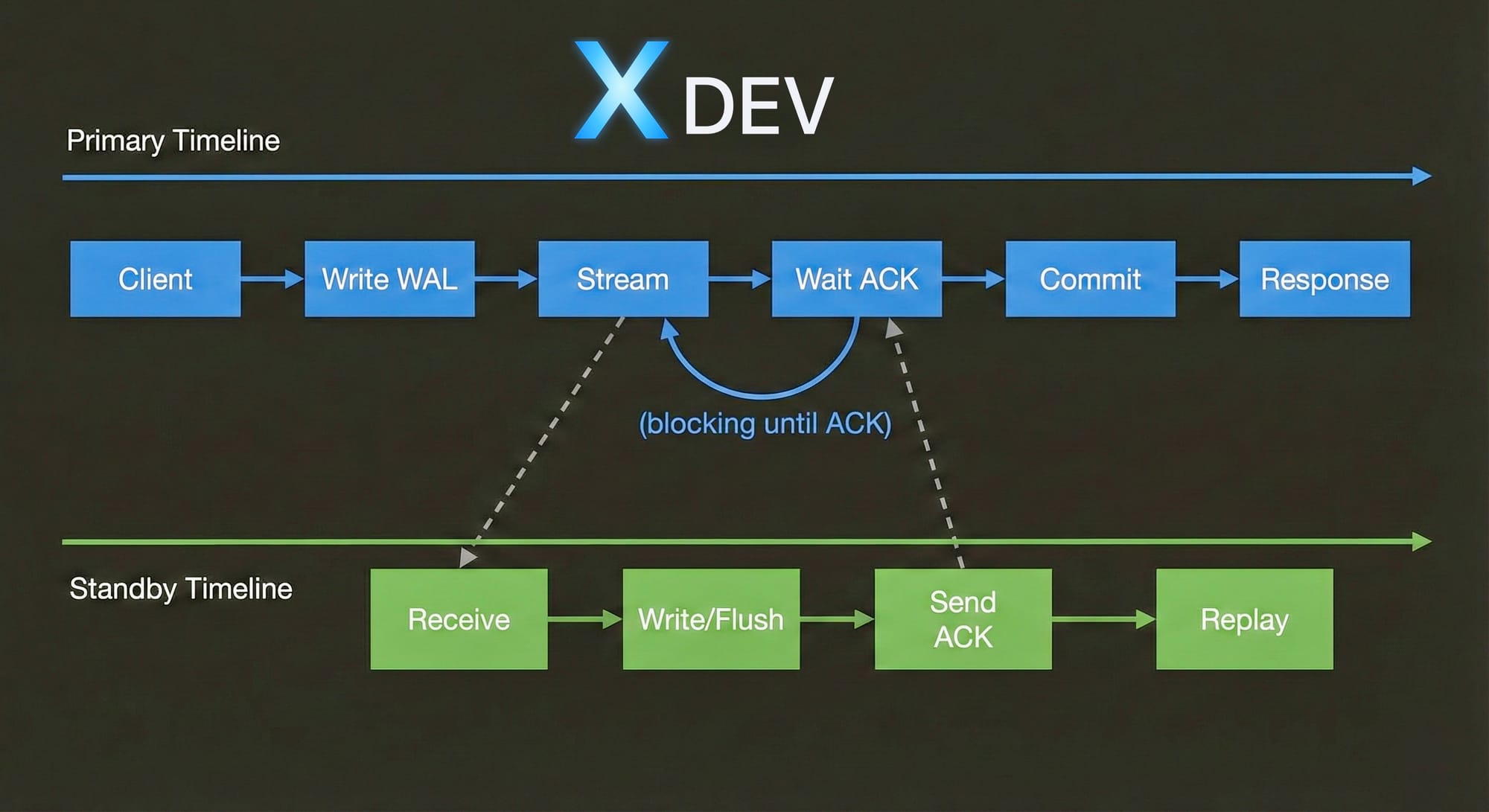
Đặc điểm:
- ✅ Zero data loss: Transaction chỉ commit khi Standby confirm
- ✅ RPO = 0: Hoàn hảo cho critical data
- ❌ Performance impact: ~2-10ms overhead mỗi commit
- ❌ Availability risk: Primary block nếu Standby fail
Configuration:
# postgresql.conf (Primary)
synchronous_commit = on # on, remote_write, remote_apply
synchronous_standby_names = 'standby1,standby2' # Tên standbys
# recovery.conf hoặc postgresql.auto.conf (Standby)
primary_conninfo = 'host=primary port=5432 user=replicator application_name=standby1'Synchronous Commit Levels:
| Level | Ý nghĩa | Data Safety | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
off | Không đợi Standby | Thấp | Cao nhất |
local | Chỉ đợi local disk | Trung bình | Cao |
remote_write | Đợi Standby write vào OS cache | Khá tốt | Trung bình |
on | Đợi Standby flush vào disk | Tốt | Chậm hơn |
remote_apply | Đợi Standby apply changes | Tốt nhất | Chậm nhất |
3.3. Quorum-based Synchronous Replication
PostgreSQL 9.6+: Flexible synchronous replication
# Chờ ANY 1 trong 2 standbys
synchronous_standby_names = 'ANY 1 (standby1, standby2)'
# Chờ FIRST 2 trong 3 standbys
synchronous_standby_names = 'FIRST 2 (standby1, standby2, standby3)'
# Chờ ALL standbys (giống cũ)
synchronous_standby_names = 'standby1, standby2'Ví dụ: ANY 1
3 Standbys: standby1 (DC1), standby2 (DC2), standby3 (DC3)
Transaction commit khi:
✅ Primary committed + ANY 1 standby acknowledged
Scenario:
- standby1: ACK trong 5ms
- standby2: ACK trong 100ms (slow network)
- standby3: DOWN
→ Transaction commit sau 5ms (chờ standby1)
→ Performance tốt + Data safety3.4. So sánh Sync vs Async
| Tiêu chí | Async | Sync |
|---|---|---|
| Commit latency | ~1ms | ~5-10ms |
| Data loss risk | Có (vài giây) | Không |
| RPO | Seconds | Zero |
| RTO | ~30-60s | ~30-60s |
| Primary performance | 100% | 95-98% |
| Network dependency | Thấp | Cao |
| Use case | Read replicas, Reporting | Critical data, Financial |
4. Replication Slots
4.1. Vấn đề trước khi có Replication Slots
Scenario:
1. Primary generates WAL files
2. Checkpoint happens → Old WAL cleaned up
3. Standby offline vài giờ
4. Standby comes back online
5. ❌ WAL files needed đã bị xóa
6. ❌ Standby không thể catch up
7. ❌ Cần rebuild Standby từ đầu4.2. Replication Slots giải quyết vấn đề
Replication Slot đảm bảo Primary giữ WAL files cho đến khi Standby consume.
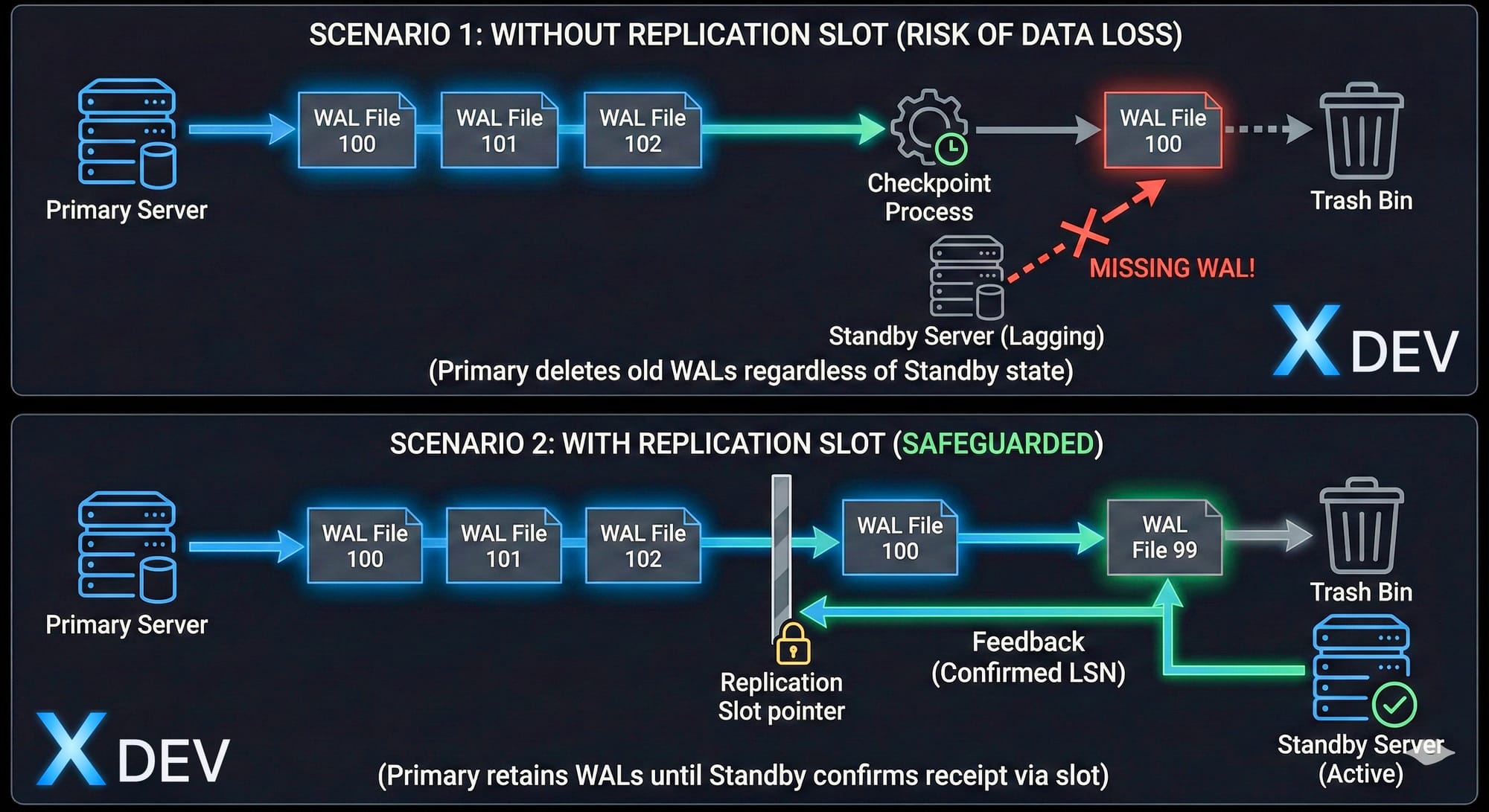
4.3. Tạo và quản lý Replication Slots
Tạo slot trên Primary:
-- Physical replication slot
SELECT * FROM pg_create_physical_replication_slot('standby1_slot');
-- Xem danh sách slots
SELECT slot_name, slot_type, active, restart_lsn, confirmed_flush_lsn
FROM pg_replication_slots;
-- Output:
slot_name | slot_type | active | restart_lsn | confirmed_flush_lsn
---------------+-----------+--------+-------------+--------------------
standby1_slot | physical | t | 0/3000000 | NULLSử dụng slot trên Standby:
ini
# postgresql.auto.conf (Standby)
primary_slot_name = 'standby1_slot'Xóa slot:
sql
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('standby1_slot');4.4. Monitoring Replication Slots
sql
-- Kiểm tra slot status
SELECT
slot_name,
active,
pg_size_pretty(pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_current_wal_lsn(), restart_lsn)) as retained_wal
FROM pg_replication_slots;
-- Cảnh báo nếu retained_wal quá lớn (>10GB)4.5. Lưu ý quan trọng
⚠️ Rủi ro:
- Nếu Standby offline lâu với slot → Primary giữ WAL mãi
- Có thể lấp đầy disk của Primary
- Cần monitoring và alert
Best practice:
sql
-- Set max WAL size để bảo vệ Primary
ALTER SYSTEM SET max_slot_wal_keep_size = '100GB'; -- PostgreSQL 13+
-- Hoặc tự động drop inactive slot sau 24h
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot(slot_name)
FROM pg_replication_slots
WHERE NOT active
AND pg_current_wal_lsn() - restart_lsn > 100*1024*1024*1024; -- 100GB5. Lab: Setup Streaming Replication thủ công
5.1. Mục tiêu Lab
Tạo PostgreSQL cluster với:
- 1 Primary server
- 1 Standby server
- Streaming replication (asynchronous)
- Hot standby (read queries)
5.2. Môi trường
Primary: 192.168.1.101 (node1)
Standby: 192.168.1.102 (node2)
PostgreSQL: 14
OS: Ubuntu 22.045.3. Bước 1: Cài đặt PostgreSQL (cả 2 nodes)
bash
# Install PostgreSQL 14
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y postgresql-14 postgresql-contrib-14
# Stop service
sudo systemctl stop postgresql5.4. Bước 2: Cấu hình Primary (node1)
Tạo replication user:
bash
sudo -u postgres psqlsql
-- Tạo user cho replication
CREATE ROLE replicator WITH REPLICATION LOGIN PASSWORD 'repl_password';
-- Exit
\qCấu hình postgresql.conf:
bash
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.confini
# Connection
listen_addresses = '*'
port = 5432
# Replication
wal_level = replica
max_wal_senders = 5
max_replication_slots = 5
wal_keep_size = 1GB
# Hot Standby (không cần cho primary nhưng tốt để có sẵn)
hot_standby = on
# Archive (optional, recommended)
archive_mode = on
archive_command = 'test ! -f /var/lib/postgresql/14/archive/%f && cp %p /var/lib/postgresql/14/archive/%f'Tạo archive directory:
bash
sudo mkdir -p /var/lib/postgresql/14/archive
sudo chown postgres:postgres /var/lib/postgresql/14/archiveCấu hình pg_hba.conf:
bash
sudo nano /etc/postgresql/14/main/pg_hba.confini
# Replication connections
host replication replicator 192.168.1.102/32 md5
host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5Start Primary:
bash
sudo systemctl start postgresql
sudo systemctl status postgresqlTạo replication slot:
bash
sudo -u postgres psqlsql
SELECT pg_create_physical_replication_slot('standby_slot');
SELECT * FROM pg_replication_slots;
\q5.5. Bước 3: Setup Standby (node2)
Stop PostgreSQL và backup data cũ:
bash
sudo systemctl stop postgresql
sudo mv /var/lib/postgresql/14/main /var/lib/postgresql/14/main.bakBase backup từ Primary:
bash
# Sử dụng pg_basebackup
sudo -u postgres pg_basebackup \
-h 192.168.1.101 \
-D /var/lib/postgresql/14/main \
-U replicator \
-P \
-v \
-R \
-X stream \
-C -S standby_slot
# Options giải thích:
# -h: Primary host
# -D: Data directory
# -U: Replication user
# -P: Show progress
# -v: Verbose
# -R: Tạo standby.signal và postgresql.auto.conf
# -X stream: Stream WAL during backup
# -C: Create replication slot
# -S: Slot nameOutput mẫu:
pg_basebackup: initiating base backup, waiting for checkpoint to complete
pg_basebackup: checkpoint completed
pg_basebackup: write-ahead log start point: 0/2000028 on timeline 1
pg_basebackup: starting background WAL receiver
pg_basebackup: created replication slot "standby_slot"
24567/24567 kB (100%), 1/1 tablespace
pg_basebackup: write-ahead log end point: 0/2000100
pg_basebackup: syncing data to disk ...
pg_basebackup: base backup completedKiểm tra standby.signal đã được tạo:
bash
ls -l /var/lib/postgresql/14/main/standby.signal
# File này đánh dấu đây là standby serverKiểm tra postgresql.auto.conf:
bash
sudo cat /var/lib/postgresql/14/main/postgresql.auto.confini
# Được tạo tự động bởi pg_basebackup -R
primary_conninfo = 'user=replicator password=repl_password host=192.168.1.101 port=5432 sslmode=prefer sslcompression=0 krbsrvname=postgres target_session_attrs=any'
primary_slot_name = 'standby_slot'Start Standby:
bash
sudo systemctl start postgresql
sudo systemctl status postgresql5.6. Bước 4: Verify Replication
Trên Primary (node1):
sql
sudo -u postgres psql
-- Kiểm tra replication status
SELECT
client_addr,
state,
sync_state,
replay_lsn,
pg_size_pretty(pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_current_wal_lsn(), replay_lsn)) as lag
FROM pg_stat_replication;
-- Output:
client_addr | state | sync_state | replay_lsn | lag
---------------+-----------+------------+-------------+-------
192.168.1.102 | streaming | async | 0/3000060 | 0 bytesTrên Standby (node2):
sql
sudo -u postgres psql
-- Kiểm tra standby status
SELECT pg_is_in_recovery(); -- Should return 't' (true)
-- Kiểm tra replication lag
SELECT
pg_last_wal_receive_lsn() AS receive,
pg_last_wal_replay_lsn() AS replay,
pg_size_pretty(pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_last_wal_receive_lsn(), pg_last_wal_replay_lsn())) AS lag;
-- Output:
receive | replay | lag
-------------+-------------+--------
0/3000060 | 0/3000060 | 0 bytes5.7. Bước 5: Test Replication
Trên Primary - Tạo test data:
sql
-- Tạo database và table
CREATE DATABASE testdb;
\c testdb
CREATE TABLE users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(100),
created_at TIMESTAMP DEFAULT NOW()
);
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES
('Alice'),
('Bob'),
('Charlie');
SELECT * FROM users;Trên Standby - Verify data:
sql
\c testdb
-- Read queries hoạt động
SELECT * FROM users;
-- Output:
id | name | created_at
----+---------+------------------------
1 | Alice | 2024-11-24 10:30:15
2 | Bob | 2024-11-24 10:30:15
3 | Charlie | 2024-11-24 10:30:15
-- Write queries bị reject
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('David');
-- ERROR: cannot execute INSERT in a read-only transaction5.8. Bước 6: Monitoring Queries
Replication delay monitoring:
sql
-- Trên Primary
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION replication_lag_bytes()
RETURNS TABLE(client_addr INET, lag_bytes BIGINT) AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN QUERY
SELECT
c.client_addr,
pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_current_wal_lsn(), c.replay_lsn)::BIGINT
FROM pg_stat_replication c;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- Sử dụng
SELECT * FROM replication_lag_bytes();Alert nếu lag > 10MB:
sql
SELECT client_addr,
pg_size_pretty(lag_bytes) as lag
FROM replication_lag_bytes()
WHERE lag_bytes > 10*1024*1024;5.9. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issue 1: Standby không connect được Primary
bash
# Check logs
sudo tail -f /var/lib/postgresql/14/main/log/postgresql-*.log
# Common errors:
# - "FATAL: password authentication failed"
# → Check pg_hba.conf và password
# - "FATAL: no pg_hba.conf entry for replication"
# → Add replication entry vào pg_hba.conf
# - Connection refused
# → Check firewall, listen_addressesIssue 2: Replication lag tăng cao
sql
-- Kiểm tra WAL sender busy
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity
WHERE backend_type = 'walsender';
-- Kiểm tra I/O trên Standby
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_bgwriter;Issue 3: Slot bị fill up disk
sql
-- Kiểm tra retained WAL
SELECT
slot_name,
pg_size_pretty(pg_wal_lsn_diff(pg_current_wal_lsn(), restart_lsn)) as retained
FROM pg_replication_slots;
-- Drop inactive slot nếu cần
SELECT pg_drop_replication_slot('standby_slot');6. Best Practices
6.1. Configuration Tuning
ini
# Primary - postgresql.conf
# Network buffer (nếu có nhiều standbys)
max_wal_senders = 10 # Tùy số standbys + 2 dự phòng
# WAL retention
wal_keep_size = 2GB # Giữ đủ WAL cho standby catch up
max_slot_wal_keep_size = 10GB # Limit slot retention (PG 13+)
# Archive (backup strategy)
archive_mode = on
archive_command = 'cp %p /backup/archive/%f'
# Checkpoint tuning
checkpoint_timeout = 15min
checkpoint_completion_target = 0.96.2. Monitoring Checklist
✅ Replication lag (bytes và time) ✅ Standby connection status ✅ WAL sender processes ✅ Disk space (pg_wal/ và archive/) ✅ Replication slots (retained WAL) ✅ Checkpoint performance
6.3. Security Recommendations
ini
# Use SSL for replication
ssl = on
ssl_cert_file = '/path/to/server.crt'
ssl_key_file = '/path/to/server.key'
# Standby connection string
primary_conninfo = '... sslmode=require sslcompression=1'ini
# pg_hba.conf - Use hostssl
hostssl replication replicator 192.168.1.0/24 md57. Tổng kết
Key Takeaways
- Streaming Replication là nền tảng của PostgreSQL HA:
- Realtime WAL streaming
- Hot Standby cho read queries
- Basis cho Patroni automated failover
- WAL (Write-Ahead Logging):
- Ghi log trước khi ghi data
- Crash recovery mechanism
- Replication transport format
- Synchronous vs Asynchronous:
- Async: Performance cao, có thể mất data
- Sync: Zero data loss, performance impact
- Quorum-based: Balance giữa 2 cái
- Replication Slots:
- Đảm bảo WAL không bị xóa sớm
- Critical cho standby stability
- Cần monitoring để tránh disk full

